Describe the Characteristics of the Floodplain Zone
Floodplains are large flat expanses of land that form on either side of a river. The floodplain is the area that a river floods onto when it exceeds bank-full capacity.

Floodplain National Geographic Society
Ad What is a FEMA high-risk flood zone.

. Rapids occur when high velocity water flows over a series of gently dipping bands of harder rock. That doesnt mean that every time theres a flood water fills the floodplain. A floodplain or flood plain is flat or nearly flat land adjacent to a stream or river that experiences occasional flooding.
The soils usually consist of levees silts and sands deposited during floods. These include but are not limited to single-family residential commercial buildings subdivision channelization irrigation structures roads bridges levees and other fills. Flood zones are geographic areas that the FEMA has defined according to varying levels of flood risk.
This reduces flood peaks and velocities and the potential for erosion. Flood Zones VE V1-30 Areas with all the characteristics of V but with base flood elevations shown at selected intervals within these. Iii They have a gently sloping gradient or flat surface.
These zones are depicted on a communitys Flood Insurance Rate Map FIRM or Flood Hazard Boundary Map. What exactly is a flood zone. Learn your Flood Risk.
Iv They have thick alluvial or fertile soils. FEMA defines Flood zones as geographic areas defined according to varying levels of flood risk. It is usually a flat area with steeper sides on the perimeter.
The 100-year floodplain and 500-year floodplain. Ii Some have braided channels. There are several types of development within the Zone A that require floodplain permits.
No base flood elevations are shown within these areas because detailed hydraulic analysis has not been performed. This elevation is called the base flood elevation BFE. Flood Insurance Program NFIP.
In turn the physical characteristics of the floodplain shape flood flows. This problem has been solved. This causes the turbulence and therefore erosive power to increase and air bubbles mix to give white water.
A floodplain can be small large and sometimes massive. Moderate to Low Risk Areas In communities that participate in the NFIP flood insurance is available to all. FEMA floodplain regulations upstream or downstream properties are not adversely impacted sufficient channel conveyance capacity is maintained or enhanced and the channel will be stable.
On open coasts the magnitude of a flood varies with the tides. Major coastal storms can significantly change the shape of shoreline land-forms making sandy coastal floodplains particularly unstable places for development. A high rate of rise for water also means less preparation time for people in the area.
It stretches from the bank s of the river to the outer edges of the valley. In coastal areas floodplain features such as beaches sand bars dunes and wetlands act as natural barriers to dissipate waves and protect back-lying areas from flooding and erosion. Increased friction as the river breaks its banks reduces the rivers efficiency to transport.
Characteristics magnitude and severity probability and frequency causative factors and locations or areas affected 1 Finally a flood hazard is the potential for inundation that involves risk to life health property and natural floodplain resources and. I Some flood plains have marshes or swamps. The BFE can be found on the FIRM and in the Flood Insurance Study FIS.
A floodplain consists of two parts. These maps divide the United States into two zones based on current flood risk. A floodplain or flood plain is an area of land adjacent to a stream or river which stretches from the banks of its channel to the base of the enclosing valley walls and which experiences flooding during periods of high discharge.
A floodplain or floodplain is a generally flat area of land next to a river or stream. V Some have deltas. Floodplain topography and soils and influence ecology.
An increase in the level of the ocean during high tide will flood larger areas than a storm that strikes during low tide. One of the main characteristics of the structure that determines the cost is the elevation of the lowest floor relative to the predicted elevation of the base flood 1 annual chance. A natural floodplain has surface conditions favoring local ponding and flood detention plus subsurface conditions favoring infiltration and storage.
The more the depth of water more will be its volume velocity and its damaging capacity. Describe the characteristics origin classification movement and modification of the six types of air masses A cP mP cT mT E. Each zone reflects the severity or type of flooding in the area.
The 100-year floodplain includes areas with a one percent probability of flooding each year and the 500-year floodplain includes areas with a 02 percent probability of flooding each year. Must be large 1000 miles uniform in horizontal dimension and must travel as unit. The Floodplain Modeling Report should be a separate document from the Drainage Report.
Answer to Solved Describe the general characteristics of a floodplain. Flood Zone V Coastal areas with a 1 or greater chance of flooding and with the additional hazard of storm waves. Vi Some have wide.
Describe and explain the formation of rapids. See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. These zones are depicted on a communitys Flood Insurance Rate Map FIRM or Flood Hazard Boundary Map.
Except in narrow steep valleys and areas of coastal bluffs floodplains provide a broad area to spread out and temporarily store floodwaters. It can be characterized by depth of inundation volume of inundation velocity of flow and rate of rise of water.
Chapter 8 Floodplain Definition And Flood Hazard Assessment
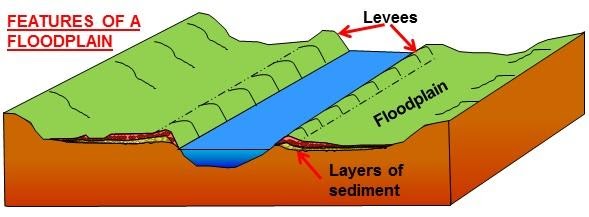
Floodplains Facts What Uses A Level Geography Notes
A State Five Characteristics Of A Flood Plain B Name Four Features Resulting From Water Action Tutorke
Comments
Post a Comment